PAG Felicitates Muslims on Commencement of Ramadan Fast
February 18, 2026TOP TEN MUSLIM UNIVERSITIES IN AFRICA
February 14, 2026ANALYSIS: Why Nigeria GDP is not the best in Africa Despite having the largest market
February 10, 2026Labour Lists Seven Demands Ahead Of Workers’ Day
Labour Lists Seven Demands Ahead Of Workers’ Day
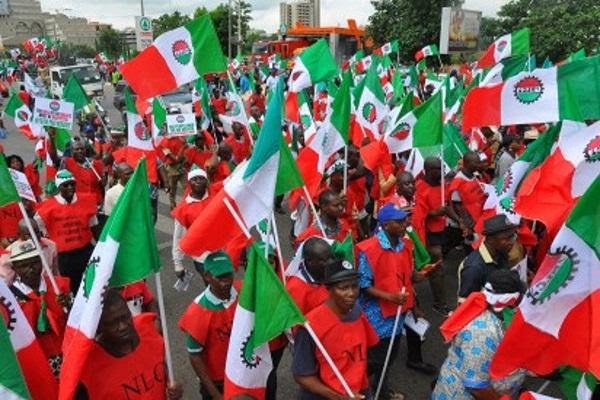

The Nigeria Labour Congress has listed seven demands from the Federal Government ahead of the May 1, 2024 Workers’ Day.
Aside from demanding for a new minimum wage, the NLC is also asking for the creation of state and local government police to tackle insecurity in the country.
The congress also stressed that states and local governments, as well as the organised private sector, must pay the new minimum wage when it is eventually approved.
International Workers’ Day, also known as Labour Day in some countries and often called May Day, is a celebration of the working class, and is marked annually on May 1, or the first Monday in May.
The 2024 Workers Day is particularly being looked forward to as it is expected that President Bola Tinubu may unveil the newly proposed minimum wage for workers in the country on that day.
Earlier in the month, organised labour had pegged the new minimum wage at N615,000 per month tentatively.
A member of the National Executive Council of the Trade Union Congress had confided in newsmen that the decision was reached before the hike in electricity tariff by the Federal Government.
The source said, “We are going to have another round of serious conversations with the government. Mind you, the tariff increase is also very good for us, because they (the government) did it when the new minimum wage process had not been concluded. So, it is going to be a good ground for us to ask for more money.”
The N30,000 subsisting minimum wage expired three days ago, as its five-year lifespan ended on April 18.
Former President Muhammad Buhari had signed the N30,000 Minimum Wage Act into law on April 18, 2019.
The tripartite committee, comprising representatives of organised private sector, organised labour and government, for a national minimum wage negotiation, follows the International Labour Organisation Convention 131.
In January, the president, through his Vice President, Kashim Shettima, had, on January 30, set up a 37-member panel at the council chamber of the State House in Abuja.
With its membership cutting across federal and state governments, the private sector, and organised labour, the panel is to recommend a new national minimum wage for the country.
In his opening address, Shettima urged members to ‘speedily’ arrive at a resolution and submit their reports early.
Chairing the panel is a former Head of the Civil Service of the Federation, Bukar Aji, who, at the inauguration ceremony, affirmed that its members would come up with a “fair, practical, implementable and sustainable” minimum wage.
The inauguration followed months of agitation from organised labour who expressed concerns over the FG’s failure to inaugurate the committee as promised during negotiations last October.
From the government’s side, members include the Minister of State for Labour and Employment, Nkeiruka Onyejeocha, representing the Minister of Labour and Employment; Minister of Finance and Coordinating Minister of the Economy, Wale Edun, who was represented by the ministry’s Permanent Secretary, Lydia Jafiya; the Minister of Budget Economic Planning, Atiku Bagudu; Head of the Civil Service of the Federation, Dr Yemi Esan; and Permanent Secretary, GSO/OSGF, Dr Nnamdi Mbaeri, amongst others.
Representing the Nigeria Governors Forum are Mohammed Bago of Niger State, representing the North Central; Senator Bala Mohammed, Governor of Bauchi State- representing the North East; Umar Dikko Radda of Katsina State, representing the North West; Prof Charles Soludo of Anambra State, representing the South East; Senator Ademola Adeleke of Osun State, from South West; and Otu Bassey of Cross River State, representing the South-South.
From the Nigeria Employers’ Consultative Association are the Director-General of NECA, Adewale-Smatt Oyerinde; Chuma Nwankwo; Thompson Akpabio; as well as members from the Nigeria Association of Chambers of Commerce, Industry, Mines and Agriculture— Michael Olawale-Cole (National President); Ahmed Rabiu (National Vice President), and Chief Humphrey Ngonadi, National Life President.
From organised labour are the NLC President, Joe Ajaero, and President of the TUC, Festus Osifo; his deputy, Tommy Etim Okon, among others.
Ajaero had announced N1m as the new minimum wage, owing to the rising inflation in the country which, according to him, had pushed many of the NLC’s members into poverty.
This led to several controversies, including experts saying that the suggested wage was unrealisable and unsustainable.
In February, Onyejeocha said the Federal Government had achieved about 90 per cent of the agreement it had with organised labour last October.
“We have done virtually everything in agreement. Ninety per cent of everything (is done),” Onyejeocha said on Channels Television’s Politics Today.
The statement came a few days before the NLC had said it would shut down the country in a nationwide protest over economic hardship.
Ajaero had told government representatives at a meeting that the protest was not about the government’s commitment to the October agreement, but inflation in the prices of food.
The minister said food security and economic prosperity were part of the priorities of the President Bola Tinubu administration.
She appealed to Nigerians to be patient with the new government as the administration was in its planting season with harvest on the horizon.
Onyejeocha said the Federal Government had ticked about 90 per cent of the 15-point memorandum of understanding it signed with organised labour on October 2, 202.
Some of the agreements include granting wage awards of N35,000 to workers, the inauguration of a minimum wage committee, and suspension of the collection of Value Added Tax on diesel for six months.
On the provision of high-capacity CNG buses for mass transit in the country, the minister said funds had been released for the purpose but “there are certain things you cannot control; you cannot control the number of days a shipment or a container will stay in the port”.
Nigeria is battling rising inflation, forex crisis, economic hardship and high cost of living occasioned by the removal of petrol subsidy, which attracted protests in parts of the country.
Speaking to our correspondent in Abuja, the NLC’s National Treasurer, Hakeem Ambali, listed seven demands the congress had made from the federal and state governments.
He said, “First, we expect that there should be improved labour government industrial relations, full implementation of minimum wage across the board for the federal, state, local government and private sector workers.
“Settlement of pension arrears, the establishment of compressed natural gas conversion centers in all senatorial districts, fixing of Port Harcourt and Kaduna refineries.
“Creation of state and local government police, granting of local government autonomy, granting of infrastructure support scheme to all local governments.”
Speaking further, Ambali noted that the Congress was still awaiting an invitation to the next meeting of the tripartite committee on minimum wage.
Meanwhile, a former two-term president of the TUC and one-time president of the Petroleum and Natural Gas Senior Staff Association of Nigeria, Peter Esele, had warned against the arbitrary fixing of a new minimum wage.
Speaking with our correspondent, Esele noted that the Federal Government and organised labour should agree on a new minimum wage before it is announced by the president on Workers’ Day to avoid another round of protests and strikes.
He said, “First, I will be surprised if organised labour says the Federal Government should announce the minimum wage. Probably the unions are hoping that by then, they will have concluded negotiations with the government. But for me, if the negotiation is not concluded by that time and the Federal Government goes ahead to announce the new national minimum wage, it is also possible that organised labour will dispute it. And what we are going to have is another round of protests and strikes.
“So my expectation for the labour unions is to put what they want on the table, while the Federal Government also puts theirs on the table. They should then both agree. But, suppose the Federal Government goes ahead and unilaterally announces a new national minimum wage, labour would oppose it, which, as I said, will lead to another round of industrial actions.
“It will be strange if the Federal Government announces the new minimum wage on Workers’ Day. However, I believe the governments are also smart enough not to make such a move unless they reach an informal agreement with the organised labour, and the Nigeria Employers’ Consultative Association”.
Esele also ruled out the possibility of problems arising if organised labour and the Federal Government fail to reach a concrete agreement on the new minimum wage by May Day.
He said, “The fact again remains that if both parties are still on the negotiation table by next month, it does not prevent the proposed new minimum wage from taking effect that month. What it simply implies is that whenever the agreement comes, the government will pay arrears.
“Even in the organised private sector, that is what we do. You can go on negotiation for even six months, but once an agreement is finally reached, and the last collective bargaining has expired, for whatever is agreed whether in six months or a year later, the arrears will be paid by the employers, which is the government in this case. So if the agreement is in place, it doesn’t matter whether they announce it on May 1 or not, the salary arrears must be paid.”
Reacting, the Director General, Manufacturers Association of Nigeria, Segun Ajayi-Kadir, stated that members of the association will pay the new minimum wage when eventually agreed to and approved.
He said, “We (the tripartite committee) are negotiating and the three groups are discussing. Whatever is agreed will be mandatory on all parties. So, the private sector is looking forward to arriving at a consensus of the committee and whatever the outcome, the private sector will oblige because we have been part of it.
“I don’t think in the history of the country, there has ever been a situation where it is the private sector that has failed to implement the minimum wage. We effectively implemented the minimum wage when it was N30,000, so there should be no apprehension whatsoever that the private sector will not pay the proposed new minimum wage. I think it is best to cross the river when one gets there.”
Meanwhile, the NLC is also demanding for the creation of state and local government police.
This demand is coming a few weeks after 16 state governors submitted reports expressing their support for establishing state police to the National Economic Council.
In the report, they also recommended changes to the constitution to allow for the creation of state police.
The reports were part of documentation received at the 140th NEC meeting presided over by Vice President Kashim Shettima at the Aso Rock Villa on Thursday, March 21.
Special Adviser to the Vice President on Media and Communications, Stanley Nkwocha, revealed that in a statement titled, ‘NEC endorses take-off of $617M i-DICE programme across states.’
According to the statement, NEC is still awaiting reports from 20 states. It expressed confidence that others would support it.
Disclosing discussions at the NEC meeting, Nkwocha said, the “Secretary to NEC (Nebeolisa Anako) made a presentation on submissions by states on the state policing initiative. Reports have been received by 16 states on the establishment of state police. 20 states have yet to send in their reports. All states across the country expressed their support for the establishment of state police.
“States made presentations in support of the creation of state police. They also recommended changes in the constitution, and the current policing structure to enable the operationalisation of the initiative.”
This comes weeks after the federal and state governments, on February 16, 2024, resolved to develop modalities to create state police to tackle the country’s security crisis.
Meanwhile, speaking with newsmen, a retired Superintendent of Police, Adebayo Alugbin, said the NLC demand for local government police resonates greatly with the call for state police creation recently made by some elder statesmen in the country.
He said, “In a federation, it is expected that the state government will control everything under it. They will be the ones to establish the police formation for each of their states and local governments. What that means is that you want people who know an area to police the area.
“From my experience, ideal policing is when you are part of the people. That is what is obtainable in Britain, whose system we copied, but wrongly operate. A policeman has to have local knowledge of the area they are covering, and that cannot be achieved without local involvement.”
Also reacting, a popular human rights lawyer, Monday Ubani, said while having locally controlled state policemen will address Nigeria’s current security challenges to a certain extent, there must be a solid legal framework that will guide the operations of the local police and guide against their abuse by state governors.
“We have been trying the over-centralised policing system for many years now without any progress in tackling insecurity. But, if we allow even local governments, if possible, and state governments, for those that are willing and have the financial capacity, to have their police, it will be good. I know people are afraid of state policing because of the overbearing nature of some of the governors. So, we must be very careful and ensure that we put legal safeguards in place that will make the governors not to abuse state police, because they may use it against the opponents.”
Meanwhile, while also commenting on how feasible the creation of local government police would be in Nigeria, a Senior Advocate of Nigeria, Shittu Wahab, explained to our Correspondent that the creation of local government police would be attainable only if the country was determined to practise the tenets of true fiscal federalism.
He said that true federalism recognised the devolution of powers and autonomy to the three tiers of government, adding that for the country to tackle the embattling issue of insecurity, there was a need for the creation of localised police to put the menace under proper surveillance.
Wahab added that a localised police would help in tackling insecurity at the grassroots, noting that most of the personnel from the federal police did not understand the languages of the local environments they were deployed to.
He said, “It will depend on whether we are determined to practice federalism, because federalism the way it is now is in the hands of the government. True federalism recognises the devolution of powers to the three tiers of government. If we must practise that, there must be autonomy for them, especially on matters of security and others.
“It now depends on if we are determined to practise true federalism, because as it is now, we are practising a unitary system, masquerading as a federalist structure. If you want to practice true fiscal federalism, I would say it is possible, but I don’t see us going that route, because there is so much over-concentration of powers at the centre. The way to go is that all crimes are local, so the more we can devote more powers to the federation units, especially in the area of policing, the more we are likely to be able to tackle the issue of crime control.”
However, another senior lawyer, Ebunolu Adegboruwa, kicked against the move, saying that the system adopted in the country showed that the country was not yet ready for such.
He advised that rather than canvassing for the creation of local government police, the organised labour should fight for how the local governments could operate without any interference or control from governors.
He said, “Without autonomy for the local governments, it is a waste of time creating an agency for the local government, whether police, civil, or anything, because the governors will not allow them to operate.
“The struggle by organised labour now should be to get autonomy for local governments, because the police for local government at this time is irrelevant and not useful, because the federal autonomy does not exert power. Even now, I don’t have any problem with the creation of state police, because this true federalism is clear that the people who are working against it have their own agenda.”
END.